简介
DeviceService在Edgex Foundry中用于连接设备,他们直接与设备打交道,可以看作是设备的驱动吧。DeviceService作用的作用有:获取设备的状态;接收处理设备发过来的数据并发送到EdgeX;变更设备配置;设备发现。
DeviceService目前有两种语言的实现,分别为GoLang版本和C版本,其中主要还是使用GoLang版本的SDK。
环境
-
EdgeX Foundry 3.0
-
go1.20.4
-
开发环境为GoLand 2023.2.2
应用步骤
1)新建一个go项目virtual-device-service-go
2)添加相关的edgexfoundry依赖
go get github.com/edgexfoundry/device-sdk-go/v3@v3.0.0
go get github.com/edgexfoundry/go-mod-core-contracts/v3@v3.0.03)创建对应的目录结构
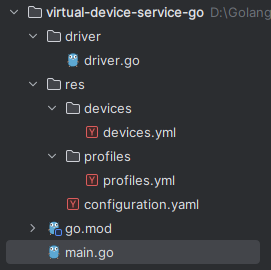
下面会针对每一个文件做说明。
4)configuration.yaml
这个是Device Service的配置文件,内容如下:
Writable:
LogLevel: INFO
Reading:
ReadingUnits: true
InsecureSecrets:
DB:
SecretName: "redisdb"
SecretData:
username: ""
password: ""
#配置客户端信息
Clients:
core-metadata:
UseMessageBus: false
#配置注册中心
Registry:
Host: "edgex-core-consul"
Port: 8500
Type: "consul"
#配置当前服务的相关信息
Service:
Host: "192.168.245.1"
Port: 59911 # Device service are assigned the 599xx range
HealthCheckInterval: "10s"
RequestTimeout: "5s"
StartupMsg: "virtual device service started"
#配置edgexfoundry的消息总线,默认是redis
MessageBus:
Protocol: "redis"
Host: "edgex-redis"
Port: 6379
Type: "redis"
AuthMode: "none"
SecretName: "redisdb"
BaseTopicPrefix: "edgex"
Optional:
ClientId: "virtual-device-service-client"
Retained: "false"
AutoReconnect: "true"
#配置设备
Device:
DataTransform: true
AsyncBufferSize: 1
MaxCmdOps: 128
MaxCmdResultLen: 256
EnableAsyncReadings: true
ProfilesDir: "./res/profiles"
DevicesDir: "./res/devices"
Discovery:
Enabled: false具体的配置项内容可以参考官网:
https://docs.edgexfoundry.org/3.0/microservices/configuration/CommonConfiguration/
https://docs.edgexfoundry.org/3.0/microservices/device/Ch-DeviceServices/
5)profiles.yml
这个文件类似于设备的物模型配置。
apiVersion: "v3"
name: "virtualDemoProfile"
manufacturer: ""
model: "Virtual-Device-Profile"
labels:
- "virtual-device-profile"
description: "虚拟模型定义"
deviceResources:
- name: "Pressure"
isHidden: true
description: "压力"
properties:
valueType: "Uint32"
readWrite: "R"
- name: "FlowVolume"
isHidden: true
description: "流量"
properties:
valueType: "Uint32"
readWrite: "R"
- name: "Speed"
isHidden: false
description: "速度"
properties:
valueType: "Uint32"
readWrite: "R"
- name: "FrameRate"
isHidden: false
description: "帧频"
properties:
valueType: "Uint32"
readWrite: "RW"
deviceCommands:
- name: "ReadResult"
readWrite: "R"
isHidden: false
resourceOperations:
- { deviceResource: "Pressure" }
- { deviceResource: "FlowVolume" }这里我配置了四个属性:Pressure、FlowVolume、Speed、FrameRate,一个设备命令:ReadResult。需要重点说明的是,其中的配置项name很重要,这个就是profiles的唯一标识。
具体的配置项含义可参考官网:
https://docs.edgexfoundry.org/3.0/microservices/device/profile/Ch-DeviceProfileRef/
6)devices.yml
这是文件是配置设备信息的,在服务启动时,会从这个文件中加载对应的设备并注册到edgexfoundry中。
deviceList:
- name: Virtual-Device-001
profileName: virtualDemoProfile
description: "虚拟设备"
protocols:
other:
Address: 192.168.10.130
Port: 3000
autoEvents:
- interval: 5s
onChange: false
sourceName: ReadResult
- interval: 6s
onChange: false
sourceName: Speed这里我定义了一个虚拟设备,并配置了自动上报的属性。其中的profileName关联的是这个设备对应的设备元信息是哪个,值就是在profiles.yml文件中配置的name。这里面的name就是设备的唯一标识。protocols是用来配置设备的协议,其实就是配置其连接信息。autoEvents配置设备需要定时上报的属性有哪些。
7)driver.go
这是文件可以说是核心实现,它是一个驱动文件,关于设备的所有控制都是通过这个文件中代码实现,下面我们看看这个文件中的具体实现:
package driver
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/edgexfoundry/device-sdk-go/v3/pkg/interfaces"
sdkModels "github.com/edgexfoundry/device-sdk-go/v3/pkg/models"
"github.com/edgexfoundry/go-mod-core-contracts/v3/clients/logger"
"github.com/edgexfoundry/go-mod-core-contracts/v3/common"
"github.com/edgexfoundry/go-mod-core-contracts/v3/models"
"math/rand"
"strconv"
"sync"
)
type Driver struct {
sdk interfaces.DeviceServiceSDK
logger logger.LoggingClient
}
var once sync.Once
var driver *Driver
func NewDriver() interfaces.ProtocolDriver {
once.Do(func() {
driver = new(Driver)
})
return driver
}
func (d *Driver) Initialize(sdk interfaces.DeviceServiceSDK) error {
d.sdk = sdk
d.logger = sdk.LoggingClient()
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) HandleReadCommands(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, reqs []sdkModels.CommandRequest) ([]*sdkModels.CommandValue, error) {
res := make([]*sdkModels.CommandValue, 0)
for _, req := range reqs {
var cv *sdkModels.CommandValue
switch req.DeviceResourceName {
case "Pressure":
cv, _ = sdkModels.NewCommandValue(req.DeviceResourceName, common.ValueTypeUint32, rand.Uint32())
case "FlowVolume":
cv, _ = sdkModels.NewCommandValue(req.DeviceResourceName, common.ValueTypeUint32, rand.Uint32())
case "Speed":
cv, _ = sdkModels.NewCommandValue(req.DeviceResourceName, common.ValueTypeUint32, rand.Uint32())
case "FrameRate":
cv, _ = sdkModels.NewCommandValue(req.DeviceResourceName, common.ValueTypeUint32, rand.Uint32())
}
res = append(res, cv)
}
return res, nil
}
func (d *Driver) HandleWriteCommands(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, reqs []sdkModels.CommandRequest, params []*sdkModels.CommandValue) error {
for i, r := range reqs {
switch r.DeviceResourceName {
case "FrameRate":
d.logger.Infof("HandleWriteCommands: deviceName: %v, resource: %v, parameters: %v, attributes: %v",
deviceName, reqs[i].DeviceResourceName, params[i], reqs[i].Attributes)
}
}
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) Stop(force bool) error {
if d.logger != nil {
d.logger.Debugf("Driver.Stop called: force=%v", force)
}
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) Start() error {
d.logger.Infof("Driver Start")
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) AddDevice(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, adminState models.AdminState) error {
d.logger.Infof("a new Device is added: %s", deviceName)
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) UpdateDevice(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, adminState models.AdminState) error {
d.logger.Infof("Device %s is updated", deviceName)
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) RemoveDevice(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties) error {
d.logger.Infof("Device %s is removed", deviceName)
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) Discover() error {
d.logger.Infof("Device Discover")
return nil
}
func (d *Driver) ValidateDevice(device models.Device) error {
protocol, ok := device.Protocols["other"]
if !ok {
return errors.New("missing 'other' protocols")
}
addr, ok := protocol["Address"]
if !ok {
return errors.New("missing 'Address' information")
} else if addr == "" {
return errors.New("address must not empty")
}
port, ok := protocol["Port"]
if !ok {
return errors.New("missing 'Port' information")
} else {
portString := fmt.Sprintf("%v", port)
_, err := strconv.ParseUint(portString, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
return errors.New("port must be a number")
}
}
return nil
}这是创建了一个结构体Driver,然后实现了驱动接口interfaces.ProtocolDriver,后面我会再说一下这个驱动接口中的各个方法是什么作用。
8)main.go
启动入口
package main
import (
"github.com/edgexfoundry/device-sdk-go/v3"
"github.com/edgexfoundry/device-sdk-go/v3/pkg/startup"
"os"
"virtual-device-service-go/driver"
)
const (
serviceName string = "virtual-device-service"
)
func main() {
//测试环境先禁用安全策略,生产环境中切不可如此使用
os.Setenv("EDGEX_SECURITY_SECRET_STORE", "false")
//这个是设置是否需要注册到注册中心的,也可以通过命令行指定
os.Setenv("EDGEX_USE_REGISTRY", "true")
deviceDriver := driver.NewDriver()
startup.Bootstrap(serviceName, device.Version, deviceDriver)
}9)执行
# 首先重构一下包依赖
go mod tidy然后执行启动main.go,就可以在edgexfoundry的控制台看到对应注册的设备服务、设备、设备元数据以及上报的数据了。
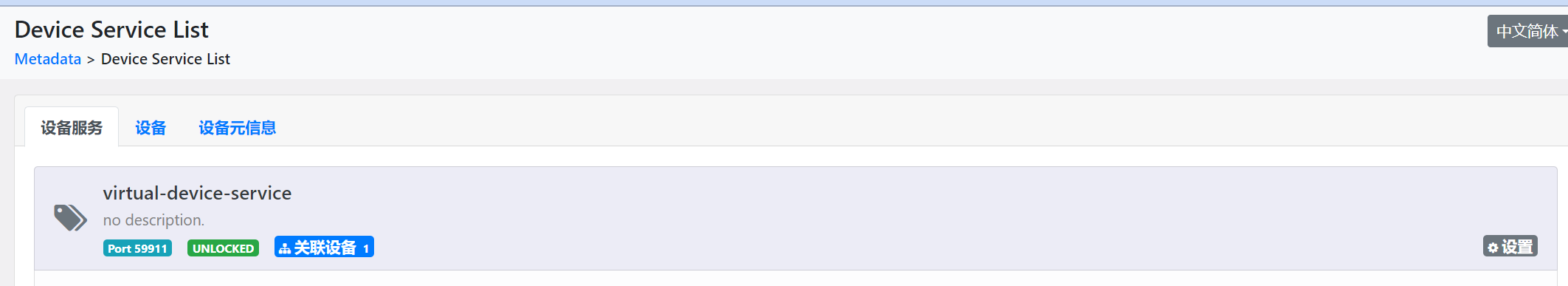
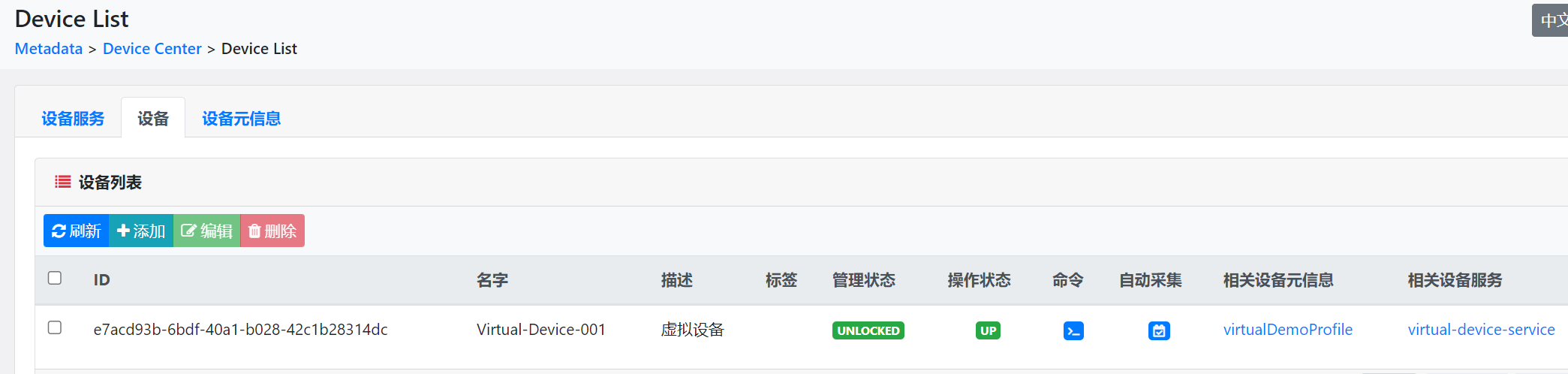
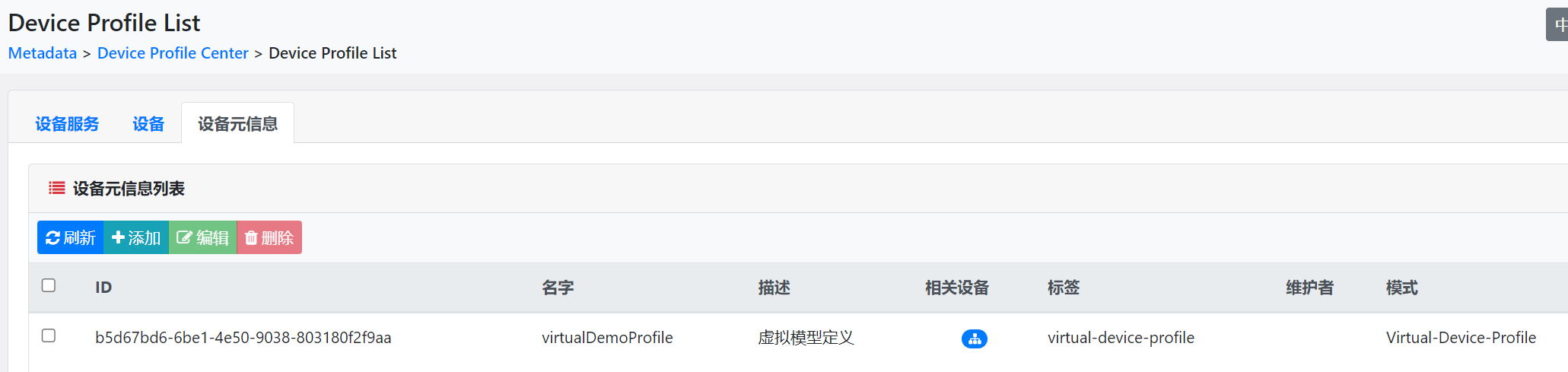
下面是设备上报的数据格式
{
"apiVersion": "v3",
"id": "e7258b93-47b2-466a-ba47-c8eeffddb143",
"deviceName": "Virtual-Device-001",
"profileName": "virtualDemoProfile",
"sourceName": "ReadResult",
"origin": 1706149800827017200,
"readings": [{
"id": "7e8fa74a-4a59-4245-ac9f-0d896bc49698",
"origin": 1706149800827017200,
"deviceName": "Virtual-Device-001",
"resourceName": "Pressure",
"profileName": "virtualDemoProfile",
"valueType": "Uint32",
"value": "1906611700"
}, {
"id": "ce137306-9580-4aab-ba64-be1aeb8ad162",
"origin": 1706149800827017200,
"deviceName": "Virtual-Device-001",
"resourceName": "FlowVolume",
"profileName": "virtualDemoProfile",
"valueType": "Uint32",
"value": "4280818086"
}]
}到此,一个设备驱动也算是开发完成了。
补充说明
下面我来具体说一下驱动接口interfaces.ProtocolDriver中各个方法的作用,先看一下源码。
// -*- Mode: Go; indent-tabs-mode: t -*-
//
// Copyright (C) 2018 Canonical Ltd
// Copyright (C) 2018-2023 IOTech Ltd
//
// SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
// Package interfaces defines interfaces and structs used to build an EdgeX Foundry Device
// Service. The interfaces provide an abstraction layer for the device
// or protocol specific logic of a Device Service, and the structs represents request
// and response data format used by the protocol driver.
package interfaces
import (
"github.com/edgexfoundry/go-mod-core-contracts/v3/models"
sdkModels "github.com/edgexfoundry/device-sdk-go/v3/pkg/models"
)
// ProtocolDriver is a low-level device-specific interface used by
// other components of an EdgeX Device Service to interact with
// a specific class of devices.
type ProtocolDriver interface {
// Initialize performs protocol-specific initialization for the device service.
// The given *AsyncValues channel can be used to push asynchronous events and
// readings to Core Data. The given []DiscoveredDevice channel is used to send
// discovered devices that will be filtered and added to Core Metadata asynchronously.
Initialize(sdk DeviceServiceSDK) error
// HandleReadCommands passes a slice of CommandRequest struct each representing
// a ResourceOperation for a specific device resource.
HandleReadCommands(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, reqs []sdkModels.CommandRequest) ([]*sdkModels.CommandValue, error)
// HandleWriteCommands passes a slice of CommandRequest struct each representing
// a ResourceOperation for a specific device resource.
// Since the commands are actuation commands, params provide parameters for the individual
// command.
HandleWriteCommands(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, reqs []sdkModels.CommandRequest, params []*sdkModels.CommandValue) error
// Stop instructs the protocol-specific DS code to shutdown gracefully, or
// if the force parameter is 'true', immediately. The driver is responsible
// for closing any in-use channels, including the channel used to send async
// readings (if supported).
Stop(force bool) error
// Start runs Device Service startup tasks after the SDK has been completely initialized.
// This allows Device Service to safely use DeviceServiceSDK interface features in this function call.
Start() error
// AddDevice is a callback function that is invoked
// when a new Device associated with this Device Service is added
AddDevice(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, adminState models.AdminState) error
// UpdateDevice is a callback function that is invoked
// when a Device associated with this Device Service is updated
UpdateDevice(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties, adminState models.AdminState) error
// RemoveDevice is a callback function that is invoked
// when a Device associated with this Device Service is removed
RemoveDevice(deviceName string, protocols map[string]models.ProtocolProperties) error
// Discover triggers protocol specific device discovery, asynchronously
// writes the results to the channel which is passed to the implementation
// via ProtocolDriver.Initialize(). The results may be added to the device service
// based on a set of acceptance criteria (i.e. Provision Watchers).
Discover() error
// ValidateDevice triggers device's protocol properties validation, returns error
// if validation failed and the incoming device will not be added into EdgeX.
ValidateDevice(device models.Device) error
}-
Initialize:就是驱动文件的初始化,在服务启动中会被调用
-
HandleReadCommands:读取设备属性值的方法
-
HandleWriteCommands:执行上层下发的设备指令
-
Stop:服务停止时会调用,用于停止连接各个设备
-
Start:在服务启动完成之后会调用,用于启动驱动程序
-
AddDevice:在有设备被添加进来的时候调用
-
UpdateDevice:设备发生变更的时候调用
-
RemoveDevice:删除设备的时候调用
-
Discover:是一个设备自动发现的方法定义
-
ValidateDevice:验证设备是否可连接的方法
针对以上的方法,我们只需要实现对应的逻辑就行了,这些方法会在相对应的逻辑中被edgexfoundry直接调用。