背景
最近遇到需要基于Qt调用python脚本的场景,所以研究了一下,特此记录。
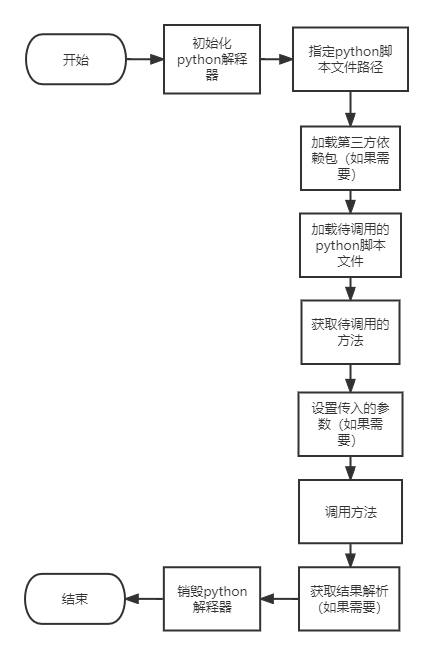
大概流程
运行环境
Windows11 x64
Qt6 6.3.1
Python-3.10.7
集成步骤
基于Qt创建一个CMakeLists项目
创建项目qt-python-demo。
引入python相关的依赖
找到你本机python安装的目录,我本机是在C盘。
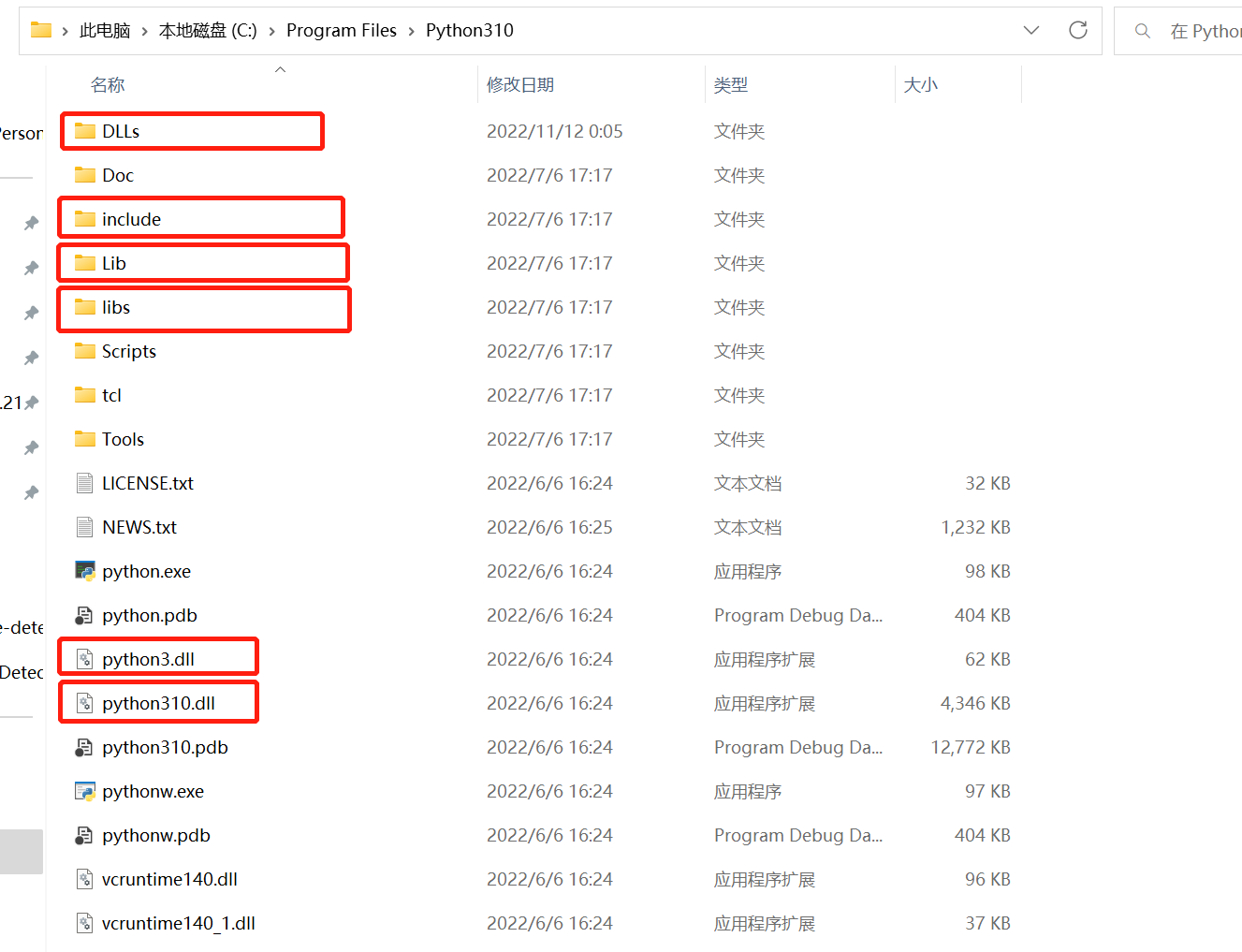
在项目根目录下创建文件夹python,将上述红框标注的文件夹复制到此文件夹下。
libs目录下,复制文件python310.lib命名为python310_d.lib,Debug模式运行时需要。
配置CMakeLists
set(PY_INCLUDE_DIR ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/python/include)
set(PY_LIB_DIR ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/python/libs)
include_directories(${PY_INCLUDE_DIR})
link_directories(${PY_LIB_DIR})
file(GLOB PY_DEPENDENCY_DIR ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/python/*.dll ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/python/DLLs ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/python/Lib)
file(COPY ${PY_DEPENDENCY_DIR} DESTINATION ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR})配置python脚本存放文件夹
1)在项目根目录下创建文件夹pyscripts,后继需要C++调用的python脚本就放在这里。
2)配置CMakeLists
file(GLOB PY_SCRIPTS ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/pyscripts)
file(COPY ${PY_SCRIPTS} DESTINATION ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR})配置python脚本第三方包依赖
1)在项目目录python/下创建文件夹site-packages,python脚本依赖的第三方包放在此文件夹下,后面有案例说明。
2)配置CMakeLists
file(GLOB PY_SITE_PACKAGES ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/python/site-packages)
file(COPY ${PY_SITE_PACKAGES} DESTINATION ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR})案例
C++在调用python脚本的时候,有返回值和无返回值在使用上还是存在一些区别,有返回值使用方法PyObject_CallObject,无返回值使用方法PyObject_CallFunction。
调用无参无返回值Python脚本
1)创建python脚本mytest.py并将其放在文件夹pyscripts下
def execWithoutParamAndResultMethod():
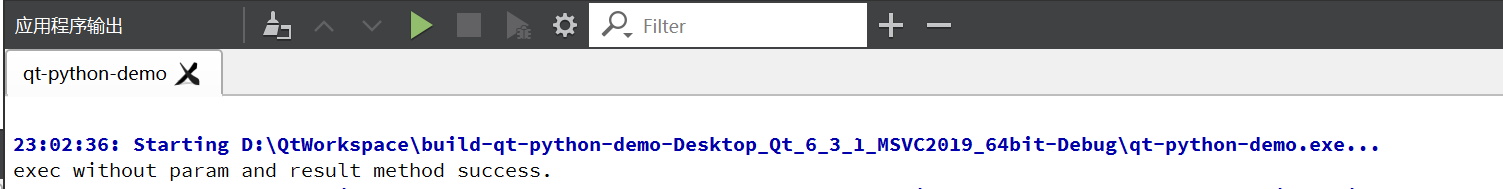
print("exec without param and result method success.")2)创建类PythonScriptHandler
pythonscripthandler.h
#ifndef PYTHONSCRIPTHANDLER_H
#define PYTHONSCRIPTHANDLER_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QException>
#pragma push_macro("slots")
#undef slots
#define PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN
#include <Python.h>
#pragma pop_macro("slots")
class PythonScriptHandler : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
PythonScriptHandler();
~PythonScriptHandler();
void execWithoutParamAndResult();
};
#endif // PYTHONSCRIPTHANDLER_Hpythonscripthandler.cpp
#include "pythonscripthandler.h"
PythonScriptHandler::PythonScriptHandler(){
}
PythonScriptHandler::~PythonScriptHandler(){
}
void PythonScriptHandler::execWithoutParamAndResult() {
try {
if(!Py_IsInitialized()) {
//python环境的初始化
Py_Initialize();
}
//初始化python系统文件路径
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./pyscripts')");
//加载待调用的python脚本文件
PyObject *pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("mytest");
if(pModule == NULL){
return;
}
//加载调用的函数
PyObject *pFunction = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "execWithoutParamAndResultMethod");
if(pFunction == NULL) {
return;
}
//执行函数
PyObject_CallFunction(pFunction, NULL);
} catch(const QException& e) {
qDebug() << e.what();
} catch(std::exception e) {
qDebug() << e.what();
}
if(Py_IsInitialized()){
//python环境的销毁,与Py_Initialize()对应
Py_Finalize();
}
}3)构建执行,查看结果
调用有参有返回值Python脚本
1)在mytest.pypython脚本中添加方法execWithParamAndResult
def execWithParamAndResult(a, b):
return a + b2)在pythonscripthandler.h添加方法声明execWithParamAndResult
class PythonScriptHandler : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
PythonScriptHandler();
~PythonScriptHandler();
void execWithoutParamAndResult();
void execWithParamAndResult();
};3)pythonscripthandler.cpp方法实现
void PythonScriptHandler::execWithParamAndResult() {
try {
if(!Py_IsInitialized()) {
//python使用环境的初始化
Py_Initialize();
}
//初始化python系统文件路径
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./pyscripts')");
//加载待调用的python脚本文件
PyObject *pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("mytest");
if(pModule == NULL){
return;
}
//加载调用的函数
PyObject *pFunction = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "execWithParamAndResult");
if(pFunction == NULL){
return;
}
//需要传入的参数
PyObject *pArgs = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 0, Py_BuildValue("i", 3));
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 1, Py_BuildValue("i", 4));
//调用函数
PyObject *pReturn = PyObject_CallObject(pFunction, pArgs);
if(pReturn == NULL){
return;
}
//解析结果
int nResult;
PyArg_Parse(pReturn, "i", &nResult);
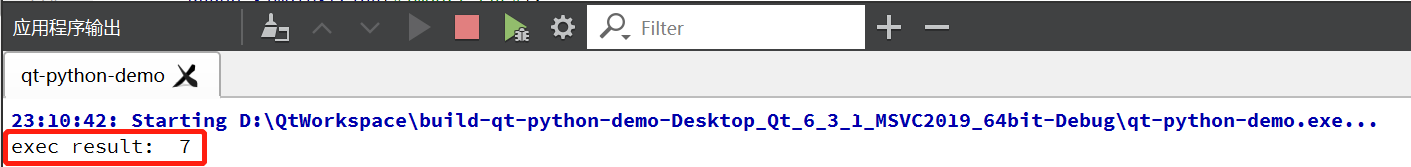
qDebug() << "exec result: " << nResult;
} catch(const QException& e) {
qDebug() << e.what();
} catch(std::exception e) {
qDebug() << e.what();
}
if(Py_IsInitialized()){
//python环境的销毁,与Py_Initialize()对应
Py_Finalize();
}
}4)构建执行,查看结果
调用依赖第三方包的Python脚本
1)在mytest.pypython脚本中添加方法execWithParamAndResultAndDependOtherLib
import json
import numpy as np
def execWithParamAndResultAndDependOtherLib(a, b):
res = np.ones([a, b])
return json.dumps(res.tolist())2)复制python包依赖
复制numpy到文件夹site-packages下面,可以到你本地的python存放包的地方找,也可以新建一个demo项目,引入就可以得到了。

3)在pythonscripthandler.h添加方法声明execWithParamAndResultAndDependOtherLib
class PythonScriptHandler : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
PythonScriptHandler();
~PythonScriptHandler();
void execWithoutParamAndResult();
void execWithParamAndResult();
void execWithParamAndResultAndDependOtherLib();
};4)pythonscripthandler.cpp方法实现
void PythonScriptHandler::execWithParamAndResultAndDependOtherLib() {
try {
if(!Py_IsInitialized()) {
Py_Initialize();
}
QString appDirPath = QCoreApplication::applicationDirPath();
//初始化python系统文件路径
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./pyscripts')");
//加载第三方依赖包
QString pyPackagesPath = "sys.path.append('" + appDirPath + "/site-packages')";
PyRun_SimpleString(pyPackagesPath.toLatin1().data());
//加载待调用的python脚本文件
PyObject *pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("mytest");
if(pModule == NULL){
return;
}
//加载调用的函数
PyObject *pFunction = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "execWithParamAndResultAndDependOtherLib");
if(pFunction == NULL){
return;
}
//需要传入的参数
PyObject *pArgs = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 0, Py_BuildValue("i", 3));
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 1, Py_BuildValue("i", 4));
//调用函数
PyObject *pReturn = PyObject_CallObject(pFunction, pArgs);
if(pReturn == NULL){
return;
}
//解析结果
char *nResult;
PyArg_Parse(pReturn, "s", &nResult);
qDebug() << "exec result: " << nResult;
} catch(const QException& e) {
qDebug() << e.what();
} catch(std::exception e) {
qDebug() << e.what();
}
if(Py_IsInitialized()){
//python环境的销毁,与Py_Initialize()对应
Py_Finalize();
}
}5)构建执行,查看结果
Py_BuildValue()使用说明
可以使用此函数构造python中的值,下面是一些例子(左侧是调用,右侧是Python值结果)(摘自python官方文档):
Py_BuildValue("") None
Py_BuildValue("i", 123) 123
Py_BuildValue("iii", 123, 456, 789) (123, 456, 789)
Py_BuildValue("s", "hello") 'hello'
Py_BuildValue("y", "hello") b'hello'
Py_BuildValue("ss", "hello", "world") ('hello', 'world')
Py_BuildValue("s#", "hello", 4) 'hell'
Py_BuildValue("y#", "hello", 4) b'hell'
Py_BuildValue("()") ()
Py_BuildValue("(i)", 123) (123,)
Py_BuildValue("(ii)", 123, 456) (123, 456)
Py_BuildValue("(i,i)", 123, 456) (123, 456)
Py_BuildValue("[i,i]", 123, 456) [123, 456]可能会遇到的问题
1)在DEBUG模式下,可能会报python310_d.lib无法找到。
可以复制一份python310.lib,重命名为python310_d.lib即可。
2)python脚本无法正确执行。
python中某个依赖包可能会存在相关的其他依赖,都需要拷贝进来,否则可能就会执行失败,比如skimage、opencv等依赖包。
3)打包到另外一台机器执行的时候可能会报Qt6Cored.dll找不到。
为了解决此问题,Qt为我们提供了一个工具windeployqt.exe,方便我们打包的时候将Qt相关的依赖都加入进来,可以在CMakeLists文件中进行配置:
get_target_property(qmake_exec_filepath Qt6::qmake IMPORTED_LOCATION)
get_filename_component(qt_exec_bin_dir ${qmake_exec_filepath} DIRECTORY)
find_program(windeployqt_exec_filepath windeployqt HINTS ${qt_exec_bin_dir})
add_custom_command(TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME} POST_BUILD
COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E env PATH="${qt_exec_bin_dir}" "${windeployqt_exec_filepath}"
"$<TARGET_FILE:${PROJECT_NAME}>"
COMMENT "Running windeployqt...")4)在初始化/销毁python解释器的时候,建议在C++的析构函数中执行销毁操作,方法中只需要检查是否需要初始化python解释器即可(遇到过如果在方法中初始化再销毁,再次调用方法的时候可能会存在些许问题)。
PythonScriptHandler::~PythonScriptHandler(){
if(Py_IsInitialized()){
Py_Finalize();
}
}